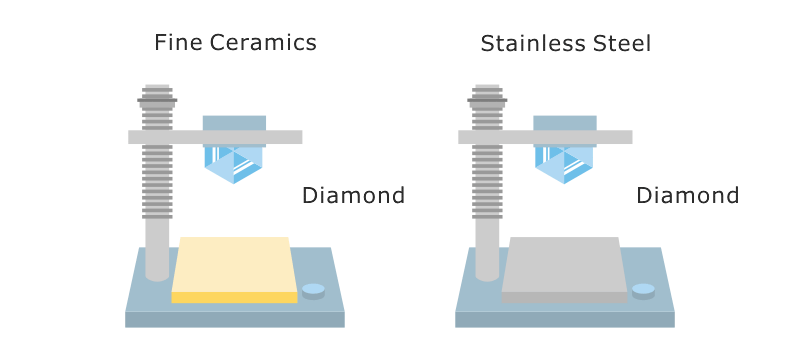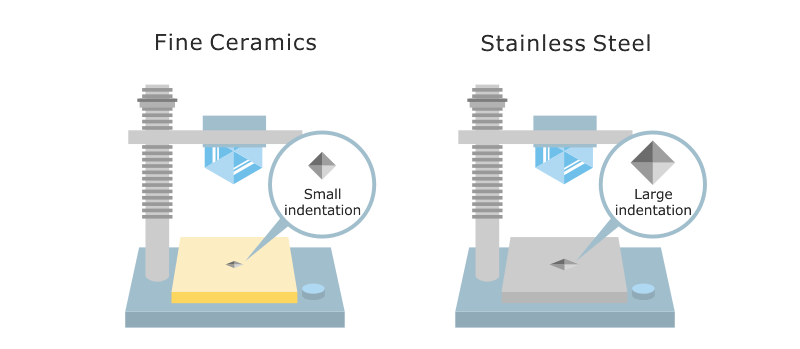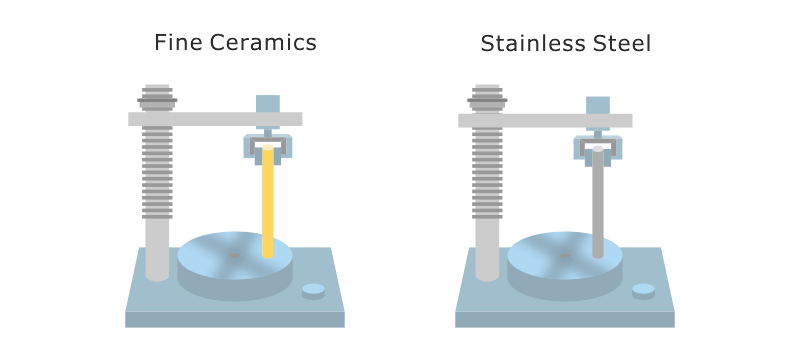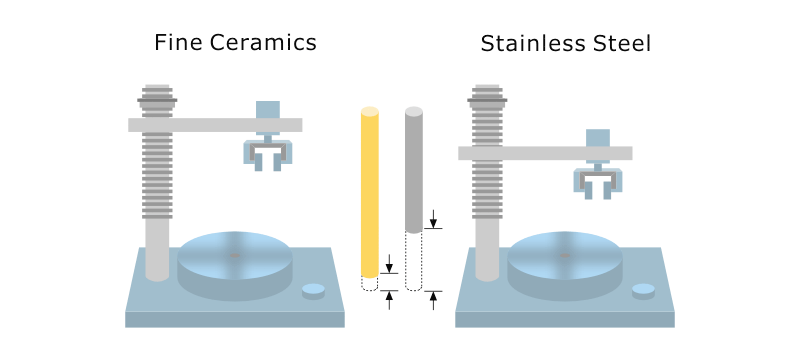
Types Of Ceramics And Their Properties

Highly electricity resistance.
Types of ceramics and their properties. Most ceramics are made up of two or more elements. Industrial ceramics are commonly understood to be all industrially used materials that are inorganic nonmetallic solids. The properties of ceramics however also depend on their microstructure. Sometimes even monocrystalline materials such as diamond and sapphire are erroneously included under the term ceramics.
The properties of ceramic materials like all materials are dictated by the types of atoms present the types of bonding between the atoms and the way the atoms are packed together. Ceramics are by definition natural or synthetic inorganic non metallic polycrystalline materials. Ceramic materials may be crystalline or partly crystalline. Ceramics tend to be rigid and brittle i e not capable of much plastic deformation.
Usually they are metal oxides that is compounds of metallic elements and oxygen but many ceramics. Ceramic composition and properties atomic and molecular nature of ceramic materials and their resulting characteristics and performance in industrial applications. Ceramic materials are inorganic non metallic materials made from compounds of a metal and a non metal. They may be as much as 96 gas by volume.
This is known as the atomic scale structure. In chemistry ceramics refer to more than simply pottery and plates. They can also be classified into three different material categories. Lower temperatures and higher crystallinity content tend to increase the modulus and the brittleness.
Ceramic foams are generally less strong than a solid ceramic but may be very strong relative to their weight. People first started making ceramics thousands of years ago pottery glass and brick are among the oldest human invented materials and we re still designing brand new ceramic materials today things like catalytic converters for today s cars and high temperature superconductors for tomorrow s computers. However their properties depend both on temperature and on the amount of crystallinity. Some ceramic foams are less brittle than their solid counterpart because air pockets may prevent cracks in the material from spreading.
They withstand chemical erosion that occurs in other materials subjected to acidic or caustic environments. This is called a compound. There s quite a big difference between age old general purpose. A ceramic material is an inorganic non metallic often crystalline oxide nitride or carbide material.
They are formed by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Let s look at each effect separately.